


Maltitol is a disaccharide polyol formed by the chemical combination of glucose and mannose, which has a sweet taste similar to sucrose. Maltitol has low hygroscopicity and excellent fluidity and crystal structure, which is used as a sugar-free ingredient or one of the sugar substitutes. It is widely applied in food and pharmaceutical industries in the form of powder or syrup beverages. Maltitol occurs naturally in fruits and vegetables. Commercially maltitol is produced from the starches of grains for example corn, wheat, and potatoes. Ingested maltitol is fermented mainly by gut microbes, which are slowly absorbed in the small intestine, resulting in a lower glycemic response and lower caloric value, which may reduce effects on diabetic patients. Moreover, the use of maltitol prevents dental caries and maintains good dental hygiene. Maltitol doesn't trigger the bacteria in your mouth to decompose sugars and starches, so it won't erode tooth enamel or cause cavities.
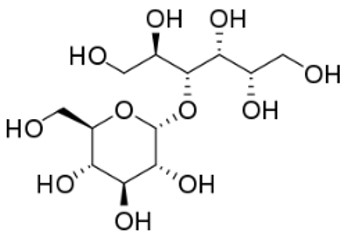 Fig.1 The structure of maltitol. (Wikipedia)
Fig.1 The structure of maltitol. (Wikipedia)
Analytical methods for the determination of maltitol in the given matrix usually involve three stages: sampling, sample preparation, and determination. It is necessary to ensure that the sample is not contaminated during collection. Sample preparation may require pre-treatment for samples, for example, homogenization, centrifugal extraction, purification, and pre-concentration steps. Proper sample preparation shortens analysis time and reduces matrix interferences.
 Fig.2 Maltitol analysis services. (CD BioGlyco)
Fig.2 Maltitol analysis services. (CD BioGlyco)
Paper Title: A novel method for the simultaneous determination of 14 sweeteners of regulatory interest using UHPLC-MS/MS
Technology: UHPLC-MS/MS
Journal: Food Additives & Contaminants
IF: 2.9
Published: 2015
Results: The authors developed a UPLC-MS/MS for the one-time simultaneous determination of 14 sweeteners of regulatory concern, including maltitol, in food and beverage matrices, which uses three isotopically labeled internal standards for quantification and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) confirmation of target analytes. All analytes were quickly separated by an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 analytical column with a mixture of aqueous and organic solvents as the mobile phase, resulting in improved method sensitivity and efficiency.
 Fig.3 MRM chromatogram of a standard solution of 14 sweeteners and three internal standards. (Shah, et al., 2015)
Fig.3 MRM chromatogram of a standard solution of 14 sweeteners and three internal standards. (Shah, et al., 2015)

CD BioGlyco has been committed to carbohydrate analysis research for many years and accumulated rich experience. We provide accurate and reproducible maltitol analysis services for our global clients. Please feel free to contact us promptly if you are interested in our analysis services.
References:
