



CD BioGlyco has developed the LiGA platform to provide clients with more comprehensive glycan interaction analysis services. In the process of LiGA Construction, attaching the glycan to the coat protein pVIII of M13 bacteriophage is a very critical step. Since there is no natural glycosylation for the M13 bacteriophage, the glycan required for the experiment needs to be attached to the bacteriophage by coupling. We use chemical or enzymatic coupling to perform the ligation, thus producing a multivalent Display of the Glycan.
 Fig.1 Conjugation strategy for glycan linking to coat protein pVIII. (CD BioGlyco)
Fig.1 Conjugation strategy for glycan linking to coat protein pVIII. (CD BioGlyco)
Glycan is chemically reactive with the reactive functional groups on pVIII. For this reason, we use chemical conjugation to attach the glycan to pVIII, forming a covalent bond between them. Depending on the specific reactive groups, we use different chemical conjugation methods, such as strain-promoted azido alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC), Cu-activated azido alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC), and so on.
Enzymatic conjugation is also an effective method to link glycans and pVIII. Under appropriate reaction conditions, we employ specific enzymes to conjugate pVIII and glycans.
We choose the appropriate conjugation strategy based on the density and structure of the glycan on pVIII. During the conjugation process, we consider the effects of experimental conditions on the stability and functionality of the glycan and pVIII. By optimizing and adjusting the experimental conditions and conjugation method, we finally achieve the ideal density of the glycan. During the experiment, we also adjust the experimental process and introduce modifications to meet the specific research needs of our clients. Finally, we verify the binding affinity and specificity of the conjugate by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Technology: Chemical conjugation
Journal: Nature Chemical Biology
IF: 16.174
Published: 2021
Results: In this study, two chemical coupling methods, SPAAC and CuAAC, were used to attach glycans to pVIII, in which CuAAC destroys phage. The phage-glycan coupling was successfully constructed using SPAAC, and finally, LiGA was successfully constructed. The results of testing the functionality of LiGA showed that the microarray could effectively monitor the binding information between glycans and glycan-binding proteins. This study provides a good association strategy for the construction of glycan arrays.
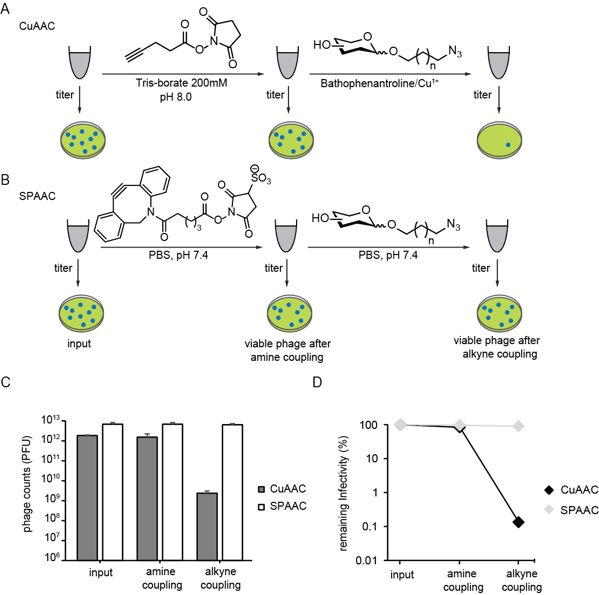 Fig.2 Toxicity of the chemical glycosylation to phage. (Sojitra, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Toxicity of the chemical glycosylation to phage. (Sojitra, et al., 2021)
CD BioGlyco is dedicated to the research of technologies related to glycan analysis. We optimize each step of the LiGA construction reaction to provide high-quality LiGA analysis services. Please feel free to contact us to learn more about glycan conjugation with coat protein pVIII. Our professional research team will surely give you the most satisfactory answer.
References
